Every researcher knows the frustration. You’ve spent months perfecting your methodology, analyzing data, and drafting your manuscript. Then comes the dreaded moment: creating figures. You open Figma or PowerPoint, stare at a blank canvas, and begin the painstaking process of dragging boxes, aligning arrows, and adjusting text that never quite looks publication-ready. Hours blur into days, and you’re still tweaking that methodology diagram.
What if an AI could read your methods section and generate publication-quality figures in seconds? That’s the promise behind PaperBanana, an agentic AI framework that’s generating considerable excitement in research communities. Developed through collaboration between leading researchers and major AI labs, PaperBanana represents a fundamental shift in how scientific illustrations are created. Rather than treating figure design as a manual graphic design task, it approaches it as an automated, intelligent process that understands scientific communication.
This comprehensive guide explores what PaperBanana AI really is, how its multi-agent system works behind the scenes, where it delivers the most value, and what limitations you should know before incorporating it into your workflow. Whether you’re a graduate student facing your first journal submission or a veteran researcher managing multiple publications, understanding PaperBanana’s capabilities can transform your approach to scientific communication.
Quick Takeaways
- PaperBanana converts method descriptions into publication-ready diagrams automatically, eliminating hours of manual design work that typically delays manuscript submissions.
- A sophisticated five-agent pipeline orchestrates planning, drafting, rendering, and self-critique to ensure figures maintain both visual appeal and scientific accuracy.
- Optimal applications include methodology workflows, neural network architectures, statistical visualizations, and conference presentation materials where consistency matters.
- Human verification remains essential for scientific integrity — automated outputs serve as high-quality drafts requiring expert review before publication.
- Early-access research previews and open-source implementations are available now through project demos, GitHub repositories, and community-built extensions.
- Users should expect occasional content inaccuracies in labels, formulas, and data representations that demand careful verification against source materials.
Understanding PaperBanana AI: More Than Just Figure Generation
When people search for “paperbanana google” or “Paperbanana ai,” they’re looking for a tool that fundamentally reimagines scientific illustration. PaperBanana isn’t simply an image generator that turns text into pictures. It’s an agentic framework — a system where multiple AI agents work together, each handling specialized tasks in the figure creation pipeline.
Think about how you currently create a methodology diagram. You read your methods section, sketch ideas on paper, open design software, select shapes and connectors, align elements, add labels, export the file, review it, and inevitably discover mistakes that send you back to step three. PaperBanana compresses this multi-hour process into minutes by automating each stage intelligently.
The framework accepts natural language inputs — a methods paragraph, a figure caption, even rough sketches — and produces publication-ready illustrations that match journal formatting standards. Recent research releases demonstrate that PaperBanana generates figures with significantly better faithfulness and aesthetic quality compared to simpler image generation models. The system doesn’t just create pretty pictures; it understands scientific communication conventions, maintains visual consistency, and produces vector-exportable formats suitable for Nature, Science, or your field’s top journals.
What makes this particularly relevant now is timing. Academic publishing pressure continues to intensify, while figure creation remains a stubborn bottleneck. Researchers report spending anywhere from 20% to 40% of manuscript preparation time on figures alone. PaperBanana addresses this pain point directly, though it’s important to understand both its capabilities and limitations before adopting it.
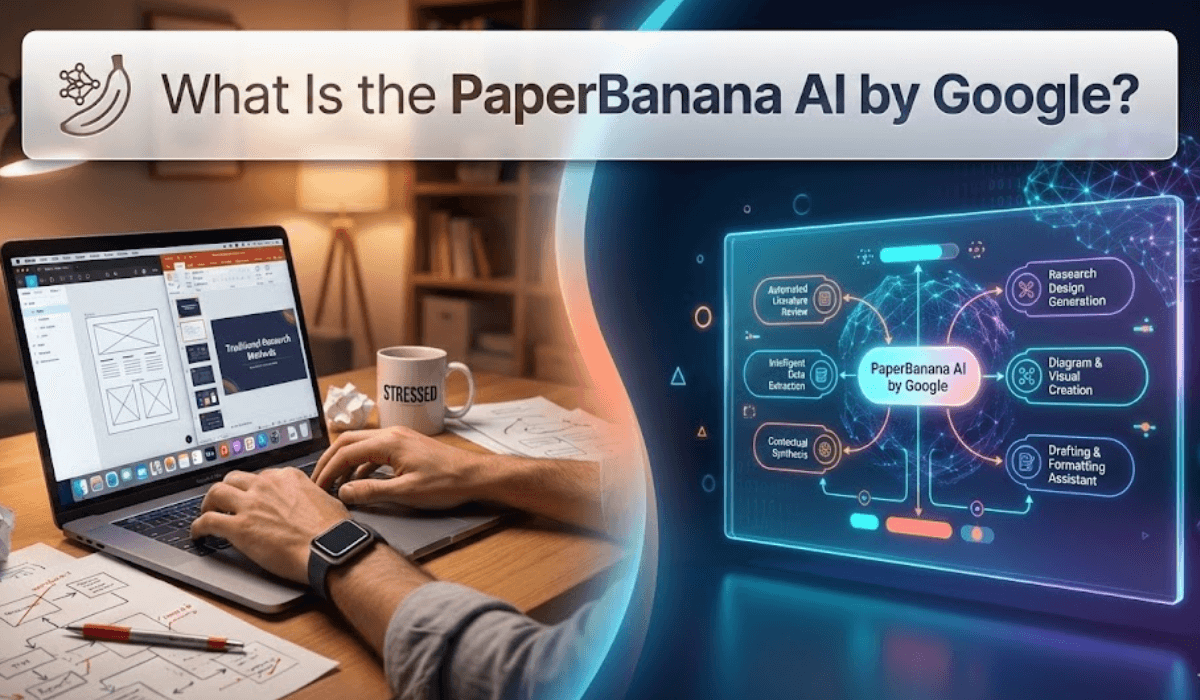
The Multi-Agent Pipeline: How PaperBanana Actually Works
PaperBanana’s real innovation lies in its orchestrated multi-agent architecture. Rather than asking a single AI model to handle everything, the system divides figure creation into specialized roles, much like a professional design team would. Understanding this pipeline helps you use PaperBanana more effectively and anticipate where human oversight adds the most value.
The process begins with a Reference Retriever agent that searches for relevant visual examples from existing publications, style guides, and user-provided samples. This agent essentially builds a visual vocabulary for your specific domain. If you’re creating a neuroscience figure, it looks at how neuroscience papers structure their diagrams. This context-awareness prevents the generic, one-size-fits-all aesthetic that plagues many automated design tools.
Next, the Planner agent transforms your unstructured method text into a structured layout blueprint. It identifies key components, determines spatial relationships, and decides what visual primitives best represent each concept. Should that data processing step be a rounded rectangle or a cylinder? Should information flow left-to-right or top-to-bottom? The Planner makes these decisions based on both your text and field-specific conventions.
The Vision-Language Model Integrator then maps semantic meanings to visual elements. This is where captions and textual descriptions get translated into iconography, symbols, and graphical representations. It’s the agent that understands “convolutional layer” should become a specific architectural element in a neural network diagram, not just generic text.
From there, the Renderer agent does the actual drawing work, using advanced image models (some implementations leverage Google’s proprietary image generation stack) to create high-fidelity shapes, connectors, and typography. Unlike simple drawing tools, this renderer understands scientific visualization requirements like consistent line weights, proper alignment grids, and legible font hierarchies.
Finally — and this is crucial — a Self-Critic agent reviews the output iteratively. It checks labels against the source text, verifies that arrows point in sensible directions, confirms alignment meets professional standards, and prompts corrections when quality thresholds aren’t met. This closed-loop refinement is why PaperBanana figures often require less manual cleanup than you’d expect from automated tools.
The entire pipeline has been evaluated using PaperBananaBench, a specialized benchmark dataset designed to test figure generation across various scientific domains. Results show measurable improvements in faithfulness to source material and visual quality compared to baseline approaches.
Read also: 750+ AI Agents Lists | AI Agents for Every Day Tasks
Real-World Applications: Where PaperBanana Shines
Understanding the theory is one thing; knowing where PaperBanana delivers practical value is what matters for your workflow. Early adopters report particularly strong results in several key areas.
Methodology diagrams represent PaperBanana’s sweet spot. Converting a methods paragraph describing your experimental pipeline into a clear visual flowchart typically consumes days of work. PaperBanana handles this in minutes, producing diagrams that show data flow, processing stages, and decision points with proper visual hierarchy. Researchers submitting to deadline-driven conferences find this especially valuable — it’s the difference between missing submission deadlines and having polished figures ready for review.
Model architecture visualizations benefit tremendously from automation. Machine learning papers routinely include complex encoder-decoder diagrams, attention mechanism illustrations, or multi-branch network architectures. These figures require the precise positioning of dozens of components. PaperBanana generates these systematically, maintaining consistent spacing, alignment, and annotation that would take hours to achieve manually in drawing software.
Statistical plots and data visualizations represent another strong use case. While tools like Matplotlib or ggplot create functional plots, achieving publication aesthetics often requires extensive styling code. PaperBanana produces publication-ready plots with proper axis labels, LaTeX-formatted equations, vector exports, and journal-appropriate styling automatically. The figures embed cleanly into manuscripts without the trial-and-error of manual formatting.
Conference materials benefit from PaperBanana’s consistency. When you’re creating posters and slide decks that need unified visual language across twenty figures, manually ensuring stylistic consistency becomes nearly impossible. PaperBanana maintains a consistent design vocabulary across all outputs, making your entire presentation feel professionally designed.
One research team shared that PaperBanana cut their figure preparation time from roughly twelve hours per manuscript to under two hours — an 83% reduction. Those gains specifically came from methodology and architecture diagrams, where the initial automated output required only minor human touchups. The time savings compound significantly for labs publishing multiple papers annually.
Limitations, Verification, and Responsible Use
PaperBanana delivers impressive results, but maintaining scientific integrity requires understanding where human oversight remains essential. No generative AI system is perfect, and figure creation carries unique responsibilities in academic publishing.
Scientific fidelity represents the primary concern. While PaperBanana excels at layout and aesthetics, it can occasionally misrepresent causal relationships, mislabel axes, or incorrectly render statistical notation. An arrow might point the wrong direction in a causal diagram. A p-value might be formatted incorrectly. An axis scale might not match your actual data range. These errors look plausible enough that they can slip past casual review, which is precisely why you must verify every detail against your original methods and data.
Hallucination risks mirror those in other generative AI systems. The model might create convincing-looking but entirely fictional labels, especially when working from ambiguous descriptions. If your methods paragraph mentions “preprocessing steps” without elaboration, PaperBanana might invent plausible-sounding preprocessing methods that don’t match what you actually did. Always treat generated figures as sophisticated drafts, not final outputs.
Attribution and copyright considerations matter when the Reference Retriever agent samples visual conventions from existing publications. While the system aims to learn style rather than copy content, you should review generated figures to ensure you’re not inadvertently replicating someone else’s proprietary diagram structure. When in doubt, verify originality or provide appropriate citations.
Field-specific conventions vary considerably. What constitutes clear scientific communication in computational neuroscience might confuse someone in organic chemistry. PaperBanana’s generic model may not capture all disciplinary nuances, especially in specialized subfields. Customization and domain-specific fine-tuning can help, but initial outputs might require significant adaptation for highly specialized contexts.
The solution isn’t avoiding PaperBanana — it’s using it responsibly. Treat generated figures as high-quality starting points that accelerate your workflow rather than replacement tools that eliminate human judgment. The best practice is establishing a human-in-the-loop verification protocol where domain experts review every automated figure before publication.
Getting Started: Practical Steps for Researchers
If PaperBanana sounds useful for your work, here’s how to approach it systematically. Start small rather than immediately using it for your most critical submissions.
Begin with a straightforward methods paragraph and a reference figure from previous work in your lab. This gives you a controlled test case where you know exactly what the output should convey. Run the generation, then carefully inspect the result. Check labels against your source text word-for-word. Verify arrows point in directions that match your described relationships. Confirm scales, units, and notations match your conventions.
Export figures in vector formats (SVG or PDF) rather than rasters. This ensures you maintain maximum flexibility for minor manual adjustments and meet journal submission requirements. Most publications require vector graphics for diagrams and illustrations anyway, so establishing this workflow from the start prevents last-minute reformatting.
Implement a coauthor review step where someone familiar with your methods but not involved in figure creation examines the output. Fresh eyes catch errors you might miss through familiarity. This peer review step, already standard in manuscript preparation, becomes even more valuable with AI-generated content.
Document your workflow transparently. If PaperBanana significantly contributed to figure creation, consider acknowledging this in your methods section or supplementary materials. Some journals now request disclosure of AI tools used in manuscript preparation. Getting ahead of these requirements demonstrates scientific integrity.
Access PaperBanana through its official research preview demo site, where you’ll find galleries of example outputs and downloadable samples. The project maintains open-source code repositories where developers have published implementations and extensions. Some research groups offer early access programs for academic users. Start with the project site and documentation to understand current capabilities and limitations before committing to production use.
The Broader Context: Scientific Communication Evolves
PaperBanana represents more than just a time-saving tool — it signals broader shifts in how scientific knowledge gets communicated. Academic publishing has seen remarkable innovation in recent years, from preprint servers to open access models to collaborative writing platforms. Figure generation automation is the latest frontier in this evolution.
Consider the parallel to statistical software. Thirty years ago, researchers computed statistics by hand or with calculators, a process prone to errors and enormously time-consuming. Statistical packages like SPSS, R, and Python didn’t eliminate the need for statistical expertise — they amplified it, allowing researchers to tackle more complex analyses and verify results more thoroughly. PaperBanana aspires to a similar impact for scientific illustration.
The technology also democratizes high-quality figure creation. Not every researcher has graphic design skills or access to professional illustrators. PaperBanana levels this playing field, ensuring that brilliant scientific work doesn’t get overlooked because the presentation falls short of publication standards. This accessibility benefit extends particularly to under-resourced institutions and early-career researchers who might lack design support.
Conclusion
PaperBanana marks a significant milestone in automating scientific illustration, transforming the tedious figure-creation process into a streamlined, intelligent workflow. Its multi-agent architecture — combining reference retrieval, planning, rendering, and self-critique — produces publication-ready diagrams that save researchers substantial time during manuscript preparation. For anyone handling multiple figures monthly, PaperBanana offers genuine productivity gains, particularly for methodology diagrams, model architectures, and statistical visualizations.
However, the technology serves best as an accelerator rather than a replacement for domain expertise. Scientific integrity demands that researchers verify generated figures against original methods and data, checking labels, scales, and relationships before submission. The optimal approach treats PaperBanana as a sophisticated drafting assistant that produces high-quality starting points for human refinement.
To explore PaperBanana responsibly, start with test cases, implement verification protocols, export vector formats, and maintain transparent documentation of AI-assisted creation. As the research preview evolves and community implementations mature, these tools will increasingly become standard infrastructure for scientific communication — much like citation managers or collaborative writing platforms today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is PaperBanana free to use, and where can I access it?
PaperBanana launched as a research preview with demo sites and open-source code repositories available through the project’s official channels. Access models vary by implementation — some offer free research previews while others require institutional partnerships. Visit the PaperBanana project site or search GitHub for community implementations to find options matching your needs. Availability continues expanding as the technology matures, with some research groups providing early access programs for academic users.
Can PaperBanana export figures suitable for journal requirements?
Yes, PaperBanana emphasizes publication-ready outputs with support for vector formats (SVG, PDF) and LaTeX-compatible labels that meet typical journal submission standards. However, you should manually verify that mathematical notation and special symbols render correctly, as some edge cases may require touchups. The system generates figures compatible with major academic publishers’ specifications, though individual journal style requirements may necessitate minor manual adjustments for spacing, font specifications, or layout conventions.
How accurate and reliable are PaperBanana’s automated diagrams?
PaperBanana demonstrates strong accuracy for layout structure and visual aesthetics, but content details — labels, numerical scales, arrow directions, statistical annotations — sometimes require human verification and correction. The self-critic agent catches many errors during generation, yet scientific fidelity ultimately depends on expert review. Treat PaperBanana outputs as high-quality drafts that need domain expert validation before publication. Accuracy improves significantly when you provide clear, detailed method descriptions and reference examples from your field.
What’s the difference between “paperbanana google,” “Paperbanana ai,” and PaperBanana?
These terms refer to the same research project and AI framework. “PaperBanana” is the official project name, while variations like “paperbanana google” and “Paperbanana ai” emerged as people search for information about the technology online. Some confusion arises because the project involves collaboration with major AI labs, including Google research teams, leading to association with Google’s brand. Regardless of the search terminology used, all these queries point to the same agentic figure-generation framework designed for academic illustration.
Where can I find technical documentation and research papers?
The PaperBanana research team published technical manuscripts on arXiv detailing the multi-agent architecture, evaluation methodology using PaperBananaBench, and performance comparisons against baseline approaches. Project documentation, code repositories, and supplementary materials appear on the official project site. For implementation details, GitHub hosts several open-source versions with varying feature sets. Academic papers provide in-depth technical specifications, while project documentation offers practical guides for researchers beginning to use the system in their workflows.